Introduction
Contamination of groundwater pollution of water caused the entry of substances such as chemicals and industrial and municipal discharges, which affect the quality compromising the usual custom.
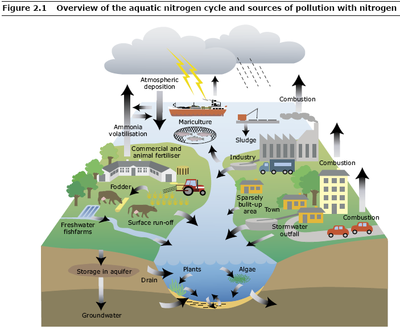
Main pollutants
Some of the major water pollutants are: waste water containing organic materials that decompose to absorb large amounts of oxygen, parasites and bacteria, fertilizers and all the substances that promote excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, pesticides and various chemicals organics (industrial waste, surfactants in detergents, by-products of decomposition of organic compounds) and petroleum and its derivatives, metals, minerals and inorganic chemicals, sand and debris washed away from agricultural land, the soil bare of vegetation, from quarries, road locations and construction sites; substances or radioactive waste from the mining of uranium and thorium and processing plants of these metals from nuclear power plants, industries and medical laboratories and research that use radioactive materials.
The heat released into the rivers from industrial plants and power through the cooling water can be considered a pollutant because it causes temperature changes that may affect the ecological balance of aquatic ecosystems and cause the death of the less-resistant organisms, increase the sensitivity of all organisms to toxic substances, reduce the ability to self-water, increase the solubility of toxic substances and encourage the development of parasites.
Effects of water pollution
The contaminants contained in water can cause many damages to human health and balance of ecosystems. The presence of nitrates (salts of nitric acid) in drinking water, for example, causes a pathological condition in children that in some cases can lead to death. Cadmium present in some sewage sludge used as fertilizer can be absorbed by the crops and bring to humans through food networks, and if taken in high doses, can cause severe diarrhea and may damage the liver and kidneys. Among the pollutants most harmful to humans, there are some heavy metals like mercury, arsenic, lead and chromium.
Lake ecosystems are particularly sensitive to pollution. The excessive input of fertilizers leaches from agricultural land can initiate a process of eutrophication, which is excessive growth of aquatic flora. The large amount of algae and aquatic plants which are to form deforms the landscape, but especially when it decomposes, consuming oxygen dissolved in water, makes asphyctic the deeper layers of the lake and produces unpleasant odors. On the bottom of the basin sediments are accumulated from various sources and water chemical reactions occur that alter the balance and composition of the ecosystem (when the waters are much limestone is, for example, the precipitation of calcium carbonate). Another source of water pollution consists of the so-called acid rain, which have already caused the disappearance of all forms of life for many lakes in northern and eastern Europe and North America.
Sources of pollution: problems and solutions
Water pollutants come mainly from municipal and industrial discharges, the processes of leaching from agricultural land and farms.
The urban waste water and industrial represent a major source of water pollution. So far, the primary objective of the disposal of urban waste has been to reduce the concentration of suspended solids, organic materials, dissolved inorganic compounds (especially those containing nitrogen and phosphorus) and harmful bacteria in the slurry placed in treatment plants, for power, then download the treated water into the environment. For some time, however, greater attention is paid to the delicate problem of the treatment and disposal of sludge that is produced in the process of purification.
In the scrubber slurry passes through three distinct phases of treatment. The first, called primary treatment, consists of a series of physical or mechanical removal of larger debris, sedimentation of suspended particles and separation of oily substances. In the second stage, called secondary treatment, it oxidizes the organic matter dispersed in the slurry by means of activated sludge and biological filters. The third stage, the tertiary treatment, is to remove the nutrients through chemical and physical processes such as adsorption on activated carbon. At each stage are produced significant amounts of sludge, the treatment and disposal accounts for 25-50% of the cost of installation and operation of a common sewage treatment plant.
Industrial discharges contain a wide variety of pollutants and their composition varies depending on the type of production process. Their impact on the environment is complex, often toxic substances contained in these discharges reinforce each other's harmful effects and thus the total damage is higher than the sum of individual effects. The concentration of pollutants can be reduced by restricting the production origin, subjecting the material to preventive treatment before downloading into the drainage system or purifying fully discharges at the same factory, catching, perhaps, the substances that can be reintroduced in the production processes .
The chemical fertilizers used in agriculture and sewage produced by the farms are rich in organic matter (containing mainly nitrogen and phosphorus) that dilavate rain, they poured into groundwater or surface water bodies. These substances are often more or less debris coarse that settle on the bottom of the basins. Often contains pathogens, the sewage of animal origin are sometimes dumped directly on the ground and from there are transported by rain into rivers, lakes and groundwater. In this case, to limit the impact of the pollutants can take simple solutions, such as the use of ponds or tanks for the purification of sewage.
Marine Pollution
The pollution of the sea due to accidental or intentional releases of oil and fuel oil, the contribution of pollutants carried by rivers and discharges to the coastal settlements. The latter, in particular, contain all sorts of contaminants (heavy metals, toxic chemicals, radioactive materials, pathogens) and often are the cause of epidemics of typhus, cholera, salmonellosis and other infectious diseases. The pollutants are carried by currents along the coasts and on the high seas, and medium and long distance. Obviously, contamination of the seas beyond the borders of the territorial waters of individual states and is the subject of international treaties that seek to limit its extent.
Oil pollution
The oil and fuel oil spilled into the sea forming on the surface of the oily film that prevents the absorption of oxygen in air, causing death of marine organisms. In oil, in addition, there are also aromatic hydrocarbons that can pose a serious threat to human health, which come through the marine food chain. The source of pollution, in this case, is given by spills of large quantities of crude oil from tankers involved in accidents, from the deliberate release of small quantities of oil by vessels of various types and loss of oil that occur during Drilling operations at the marine oil platforms. It is estimated that for every million tons of oil transported by sea, one ton is dispersed as a result of spills of various kinds, although the greatest danger is from accidents that often involve the super.
Main pollutants
Some of the major water pollutants are: waste water containing organic materials that decompose to absorb large amounts of oxygen, parasites and bacteria, fertilizers and all the substances that promote excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, pesticides and various chemicals organics (industrial waste, surfactants in detergents, by-products of decomposition of organic compounds) and petroleum and its derivatives, metals, minerals and inorganic chemicals, sand and debris washed away from agricultural land, the soil bare of vegetation, from quarries, road locations and construction sites; substances or radioactive waste from the mining of uranium and thorium and processing plants of these metals from nuclear power plants, industries and medical laboratories and research that use radioactive materials.
The heat released into the rivers from industrial plants and power through the cooling water can be considered a pollutant because it causes temperature changes that may affect the ecological balance of aquatic ecosystems and cause the death of the less-resistant organisms, increase the sensitivity of all organisms to toxic substances, reduce the ability to self-water, increase the solubility of toxic substances and encourage the development of parasites.
Effects of water pollution
The contaminants contained in water can cause many damages to human health and balance of ecosystems. The presence of nitrates (salts of nitric acid) in drinking water, for example, causes a pathological condition in children that in some cases can lead to death. Cadmium present in some sewage sludge used as fertilizer can be absorbed by the crops and bring to humans through food networks, and if taken in high doses, can cause severe diarrhea and may damage the liver and kidneys. Among the pollutants most harmful to humans, there are some heavy metals like mercury, arsenic, lead and chromium.
Lake ecosystems are particularly sensitive to pollution. The excessive input of fertilizers leaches from agricultural land can initiate a process of eutrophication, which is excessive growth of aquatic flora. The large amount of algae and aquatic plants which are to form deforms the landscape, but especially when it decomposes, consuming oxygen dissolved in water, makes asphyctic the deeper layers of the lake and produces unpleasant odors. On the bottom of the basin sediments are accumulated from various sources and water chemical reactions occur that alter the balance and composition of the ecosystem (when the waters are much limestone is, for example, the precipitation of calcium carbonate). Another source of water pollution consists of the so-called acid rain, which have already caused the disappearance of all forms of life for many lakes in northern and eastern Europe and North America.
Sources of pollution: problems and solutions
Water pollutants come mainly from municipal and industrial discharges, the processes of leaching from agricultural land and farms.
The urban waste water and industrial represent a major source of water pollution. So far, the primary objective of the disposal of urban waste has been to reduce the concentration of suspended solids, organic materials, dissolved inorganic compounds (especially those containing nitrogen and phosphorus) and harmful bacteria in the slurry placed in treatment plants, for power, then download the treated water into the environment. For some time, however, greater attention is paid to the delicate problem of the treatment and disposal of sludge that is produced in the process of purification.
In the scrubber slurry passes through three distinct phases of treatment. The first, called primary treatment, consists of a series of physical or mechanical removal of larger debris, sedimentation of suspended particles and separation of oily substances. In the second stage, called secondary treatment, it oxidizes the organic matter dispersed in the slurry by means of activated sludge and biological filters. The third stage, the tertiary treatment, is to remove the nutrients through chemical and physical processes such as adsorption on activated carbon. At each stage are produced significant amounts of sludge, the treatment and disposal accounts for 25-50% of the cost of installation and operation of a common sewage treatment plant.
Industrial discharges contain a wide variety of pollutants and their composition varies depending on the type of production process. Their impact on the environment is complex, often toxic substances contained in these discharges reinforce each other's harmful effects and thus the total damage is higher than the sum of individual effects. The concentration of pollutants can be reduced by restricting the production origin, subjecting the material to preventive treatment before downloading into the drainage system or purifying fully discharges at the same factory, catching, perhaps, the substances that can be reintroduced in the production processes .
The chemical fertilizers used in agriculture and sewage produced by the farms are rich in organic matter (containing mainly nitrogen and phosphorus) that dilavate rain, they poured into groundwater or surface water bodies. These substances are often more or less debris coarse that settle on the bottom of the basins. Often contains pathogens, the sewage of animal origin are sometimes dumped directly on the ground and from there are transported by rain into rivers, lakes and groundwater. In this case, to limit the impact of the pollutants can take simple solutions, such as the use of ponds or tanks for the purification of sewage.
Marine Pollution
The pollution of the sea due to accidental or intentional releases of oil and fuel oil, the contribution of pollutants carried by rivers and discharges to the coastal settlements. The latter, in particular, contain all sorts of contaminants (heavy metals, toxic chemicals, radioactive materials, pathogens) and often are the cause of epidemics of typhus, cholera, salmonellosis and other infectious diseases. The pollutants are carried by currents along the coasts and on the high seas, and medium and long distance. Obviously, contamination of the seas beyond the borders of the territorial waters of individual states and is the subject of international treaties that seek to limit its extent.
Oil pollution
The oil and fuel oil spilled into the sea forming on the surface of the oily film that prevents the absorption of oxygen in air, causing death of marine organisms. In oil, in addition, there are also aromatic hydrocarbons that can pose a serious threat to human health, which come through the marine food chain. The source of pollution, in this case, is given by spills of large quantities of crude oil from tankers involved in accidents, from the deliberate release of small quantities of oil by vessels of various types and loss of oil that occur during Drilling operations at the marine oil platforms. It is estimated that for every million tons of oil transported by sea, one ton is dispersed as a result of spills of various kinds, although the greatest danger is from accidents that often involve the super.

This kind of weather was predicted by scientist, Mojib Latif who last year predicted that earth was going to cool off for the next 20-30 years.The cooling would be the result of changes to ocean currents and temperatures in the North Atlantic, a feature known as the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and the NAO may be partly the cause of warming during the past 30 years.
ReplyDeletepredict science
prdictions
who is edgar casey
cayce edga
are edgar cayce
what is the environment
environment topics
environment
seminar topics
water pollution
topics on the environment
topics for environment